Publication 2004

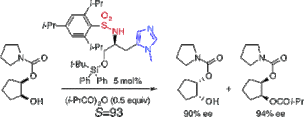
▼Rational Design of an L-Histidine-Derived Minimal Artificial Acylase for the Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Alcohols
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Yuji Kosugi
Matsujiro Akakura
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126 (39), 12212-12213.
This communication describes the rational design of an L-histidine-derived minimal artificial acylase. Our new artificial acylase, tert-butyldiphenylsilyl ether of N-(2,4,6-triisopropylbenzenesulfonyl)-pi(Me)-L-histidinol, is a simple and small molecule (molecular weight = 660) that contains only one chiral carbon center that originates from natural L-histidine. The kinetic acylation of racemic secondary alcohols induced by this compound showed an S (kfast/kslow) value of up to 93. A reusable polystyrene-bound artificial acylase was also developed to examine its practical usability.
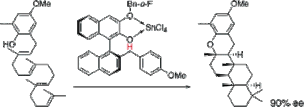
▼A New Artificial Cyclase for Polyprenoids: Enantioselective Total Synthesis of (-)-Chromazonarol, (+)-8-epi-Puupehedione, and (-)-11'-Deoxytaondiol Methyl Ether
Hideaki, Ishibashi
Kazuaki, Ishihara*
Hisashi, Yamamoto*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2004, 126 (36), 11122-11123.
This paper describes a new artificial cyclase, optically pure 3-o-fluorobenzyloxy-2-hydroxy-2'-(p-methoxybemzyl)-1,1'-binaphthyl・SnCl4, which is effective for the enantioselective cyclization of 2-(polyprenyl)phenol derivatives to afford polycyclic terpenoids bearing a chroman skeleton such as (-)-chromazonarol, (+)-8-epi-puupehedione, a key synthetic intermediate of (+)-wiedendiol, and (-)-11'-deoxytaondiol methyl ether.

▼Water-Tolerant and Reusable Catalysts for Direct Ester Condensation between Equimolar Amounts of Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols
Masaya Nakayama
Atsushi Sato
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Adv. Synth. Catal. 2004, 346, 1275-1279.
ZrOCl28H2O and HfOCl28H2O are highly effective, water-tolerant, and reusable homogeneous catalysts for direct ester condensation between equimolar amounts of carboxylic acids and alcohols. Notably, zirconium(IV) salts such as ZrOCl28H2O and Zr(OAc)x(OH)y are potential green catalysts due to their low toxicity, commercial availability at low cost, ease of handling, high catalytic activity, and reusability.
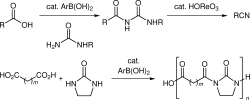
▼Arylboronic Acid-Catalyzed Direct Condensation of Carboxylic Acids with Ureas
Toshikatsu Maki
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Synlett 2004, 1355-1358.
The first example of the catalytic direct condensation of carboxylic acids with ureas to give N-acylureas, N,N'-diacyl-2-imidazolidones, and poly(N,N'-diacyl-2-imidazolidone)s is described. Arylboronic acids bearing electron-withdrawing substituents are highly effective as catalysts for this condensation. Furthermore, a new and efficient one-pot procedure for the conversion of carboxylic acids and urea to nitriles via N-acylurea intermediates was accomplished by using arylboronic acid and rhenium(VII) oxo complexes as hybrid catalysts.
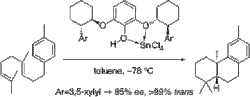
▼Tin(IV) Chloride-Chiral Pyrogallol Derivatives as New Lewis Acid-Assisted Chiral Bronsted Acids for Enantioselective Polyene Cyclization
Keiko Kumazawa
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 2551-2554.
New Lewis acid-assisted Bronsted acids (LBAs), tin(IV) chloride-2,6-dialkoxyphenols, serve as artificial cyclases for biomimetic polyene cyclization. For example, the enantioselective cyclization of 4-(homogeranyl)toluene using tin(IV) chloride-2,6-di[(1'R,2'R)-trans-2'-(3'',5''-xylyl)cyclohexanoxy]-phenol gave a trans-fused tricyclic compound with 85% ee.
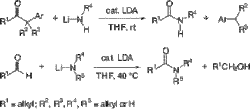
▼Synthesis of Carboxamides by LDA-Catalyzed Haller-Bauer and Cannizzaro Reactions
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Takayuki Yano
Org. Lett. 2004, 6, 1983-1986.
The first direct synthesis of N-alkylcarboxamides and N,N-dialkylcarboxamides by Haller-Bauer (HB) and Cannizzaro-type reactions has been realized. Lithium N,N-diisopropylamide (LDA) catalyst was successfully used in not only the HB reaction of benzylic ketones with lithium N-alkylamides to give the corresponding carboxamides and hydrocarbons but also in the Cannizzaro-type reaction of aldehydes with lithium N-alkylamides or lithium N,N-dialkylamides to give the corresponding carboxamides and alcohols.

▼Asymmetric Direct Aldol Reaction Assisted by Water and a Proline-Derived Tetrazole Catalyst
Hiromi Torii
Masakazu Nakadai
Kazuaki Ishihara
Susumu Saito*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 1983-1986.
Just add water to improve the performance of direct aldol reactions like that shown. Previously, aldehydes with high water-affinity or -solubility were considered unsuitable for asymmetric synthesis.

▼Asymmetric Vinylogous Direct Aldol Reaction Using Aluminum Tris[2,6-bis(4-alkylphenyl)phenoxide]
Hiroshi Takikawa
Kazuaki Ishihara
Susumu Saito*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Synlett 2004, 732-734.
Diastereoselective vinylogous direct aldol reaction was realized by use of chiral a,b-unsaturated esters and aldehydes in the presence of aluminum tris[2,6-bis(4-alkylphenyl)phenoxide]s. The reaction involves novel 1,7-asymmetric induction and direct coupling of an a,b-unsaturated ester with an aldehyde, through in situ deprotonation of the a-proton of the ester component by LTMP.

▼Chiral Molecular Recognition by Aluminum Tris(2,6-diphenylphenoxide) in an Asymmetric 1,4-Addition
Hirotsugu Ito
Takashi Nagahara
Kazuaki Ishihara
Susumu Saito*
Hisashi Yamamoto*
Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2004, 43, 994-997.
A precomplex of a chiral α,β-unsaturated ester and a bulky aluminum oxide is crucial to setting the diastereoselectivity in the 1,4-addition of a Grignard or organolithium reagent. This approach based on chiral recognition broadens the potential of the strategies relying on stoichiometric reagents.







