論文 2009

▼Rational Design of Highly Effective Asymmetric Diels-Alder Catalysts Bearing 4,4′-Sulfonamidomethyl Groups
Akira Sakakura
Rei Kondo
Yuki Matsumura
Matsujiro Akakura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 17762-17764.
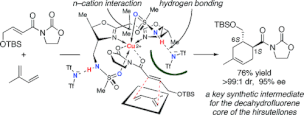
The rational design of bis(oxazoline)-copper(II) catalysts based on postulated intramolecular secondary n-cation interaction for the highly enantioselective Diels-Alder reaction is presented. A theoretical calculation suggested that the n electrons of the 4,4'-sulfonamidomethyl groups successfully interact with the Cu(II) cation and that the counteranions with protons of sulfonamido groups. These secondary interactions might be essential for the high catalytic activity, the broad range of substrates, and the high level of induction of the enantioselectivity.
▼Rational Design of Dynamic Ammonium Salt Catalysts towards More Fexible and Selective Function
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Proc. Jpn. Acad., Ser. B 2009, 85(8), 290-313.
▷https://doi.org/10.2183/pjab.85.290
▼IBS-Catalyzed Oxidative Rearrangement of Tertiary Allylic Alcohols to Enones with Oxone
Muhammet Uyanik
Ryota Fukatsu
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 3470-3473.
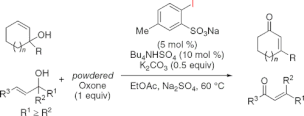
A 2-iodoxybenzenesulfonic acid (IBS)-catalyzed oxidative rearrangement of tertiary allylic alcohols to enones with powdered Oxone in the presence of potassium carbonate and tetrabutylammonium hydrogen sulfate has been developed.

▼3-Pyrroline-1-carbonyl (Pyroc) Group: A Removable Protecting Group for the Kinetic Resolution of Racemic Carboxylic Acids and Alcohols through Catalytic Asymmetric Acylation
Akira Sakakura
Shuhei Umemura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Synlett 2009, 1647-1650.
The O-3-pyrroline-1-carbonyl (O-Pyroc) group and 3-pyrrolinamide are useful removable protecting groups for the kinetic resolution of racemic α-hydroxycarboxylic acids, β-hydroxy-carboxylic acids, 1,2-dicarboxylic acids, and 1,2-diols using the l-histidine-derived bifunctional catalysts. The Pyroc group can be easily introduced from Pyroc chloride. Selective deprotection of the Pyroc group and 3-pyrrolinamide can be carried out via DDQ oxidation followed by hydrolysis using sodium hydroxide, without epimerization.
▼Chiral Lanthanum(III)-Binaphthyldisulfonate Complexes for Catalytic Enantioselective Strecker Reaction
Manabu Hatano
Yasushi Hattori
Yoshiro Furuya
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Org. Lett. 2009, 11, 2321-2324.
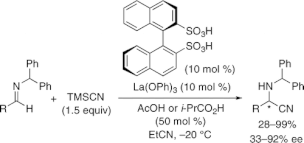
A catalytic enantioselective Strecker reaction catalyzed by novel chiral lanthanum(III)-binaphthyl disulfonate complexes was developed. The key to promoting the reactions was a semistoichiometric amount of AcOH or i-PrCO2H, which takes advantage of HCN generation in situ. The corresponding cyanation products were obtained in high yields and with high enantioselectivities.

▼Hypervalent Iodine-Catalyzed Oxylactonization of Ketocarboxylic Acids to Ketolactones
Muhammet Uyanik
Takeshi Yasui
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009, 19(14), 3848-3851.
(Special Symposium-in-Print: the 2009 Tetrahedron Young Investigator Award in Bioorgaic and Medicinal Chemistry in honor of its recipient Professor Carlos F. Barbas)
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.bmcl.2009.03.148
The hypervalent iodine-catalyzed oxylactonization of ketocarboxylic acids to ketolactones was achieved in the presence of iodobenzene (10 mol %), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (20 mol %) and metachloroperbenzoic acid as a stoichiometric co-oxidant.
▼Hypervalent Iodine-Mediated Oxidation of Alcohols
Muhammet Uyanik
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Chem. Commun. 2009, 2086-2099
The hypervalent iodine-catalyzed oxylactonization of ketocarboxylic acids to ketolactones was achieved in the presence of iodobenzene (10 mol %), p-toluenesulfonic acid monohydrate (20 mol %) and metachloroperbenzoic acid as a stoichiometric co-oxidant.

▼Highly Efficient Synthesis of Functionalized Tertiary Alcohols Catalyzed by Potassium Alkoxide-Crown Ether Complexes
Manabu Hatano
Shinji Suzuki
Eri Takagi
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Tetrahedron Lett. 2009, 50, 3171-3174.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tetlet.2009.01.028
A highly efficient Mukaiyama aldol reaction between ketones and trimethylsilyl enolates in the presence of potassium alkoxide-crown ether complexes as Lewis base catalysts (0.3-5 mol %), which minimized the competing retro-aldol reaction, was developed. These catalysts promoted other addition reactions of trimethylsilyl reagents to ketones and aldimines, such as silyltrifluoromethylation, silylcyanation, and silylphosphonylation. A direct hydrophosphonylation of ketones also proceeded when the catalysts were used as a Bronsted base under mild reaction conditions.

▼Dehydrative Cyclization of Serine, Threonine, and Cysteine Residues Catalyzed by Molybdenum(VI) Oxo Compounds
Akira Sakakura
Rei Kondo
Shuhei Umemura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 2102-2109.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.12.074
Commercially available molybdenum(VI) oxides such as (NH4)2MoO4, (NH4)6Mo7O24・4H2O, MoOz(acac)2, and MoO2(TMHD)2 are highly effective dehydrative cyclization catalysts for the synthesis of a variety of oxazolines. The reaction proceeds with a complete retention of configuration at the bata-position. For the dehydrative cyclization of cysteine derivatives, bis(2-ethyl-8-quinolinolato)dioxomolybdenum(VI) shows remarkable catalytic activity and gives thiazolines without a significant loss of stereochemical integrity at the C2-exomethine positions.

▼Dehydrative Condensation Catalyses
Kazuaki Ishihara*
Tetrahedron 2009, 65, 1085-1109.
▷http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.tet.2008.11.004
This report focuses on the catalytic dehydrative condensation reactions of carboxylic acids and phosphoric acids with alcohols and amines to give esters and amides without the activation of acids with stoichiometric condensing agents.
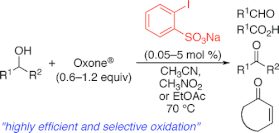
▼Iodoxybenzenesulfonic Acid as an Extremely Active Catalyst for the Selective Oxidation of Alcohols to Aldehydes, Ketones, Carboxylic Acids, and Enones with Oxone
Muhammet Uyanik
Matsujiro Akakura
Kazuaki Ishihara*
J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2009, 131, 251-262.
▷DOI: 10.1021/ja806846q
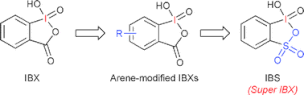
Electron-donating group-substituted 2-iodoxybenzoic acids (IBXs) such as 5-Me-IBX (1g), 5-MeO-IBX (1h), and 4,5-Me2-IBX (1i) were superior to IBX 1a as catalysts for the oxidation of alcohols with Oxone (a trademark of DuPont) under nonaqueous conditions, although Oxone was almost insoluble in most organic solvents. The catalytic oxidation proceeded more rapidly and cleanly in nitromethane. Furthermore, 2-iodoxybenzenesulfonic acid (IBS, 6a) was much more active than modified IBXs. Thus, we established a highly efficient and selective method for the oxidation of primary and secondary alcohols to carbonyl compounds such as aldehydes, carboxylic acids, and ketones with Oxone in nonaqueous nitromethane, acetonitrile, or ethyl acetate in the presence of 0.05−5 mol % of 6a, which was generated in situ from 2-iodobenzenesulfonic acid (7a) or its sodium salt. Cycloalkanones could be further oxidized to α,β-cycloalkenones or lactones by controlling the amounts of Oxone under the same conditions as above. When Oxone was used under nonaqueous conditions, Oxone wastes could be removed by simple filtration. Based on theoretical calculations, we considered that the relatively ionic character of the intramolecular hypervalent iodine−OSO2 bond of IBS might lower the twisting barrier of the alkoxyperiodinane intermediate 16.







